Bolt V1
Here is a high-level overview of the transaction flow to obtain an inclusion preconfirmation with Bolt:
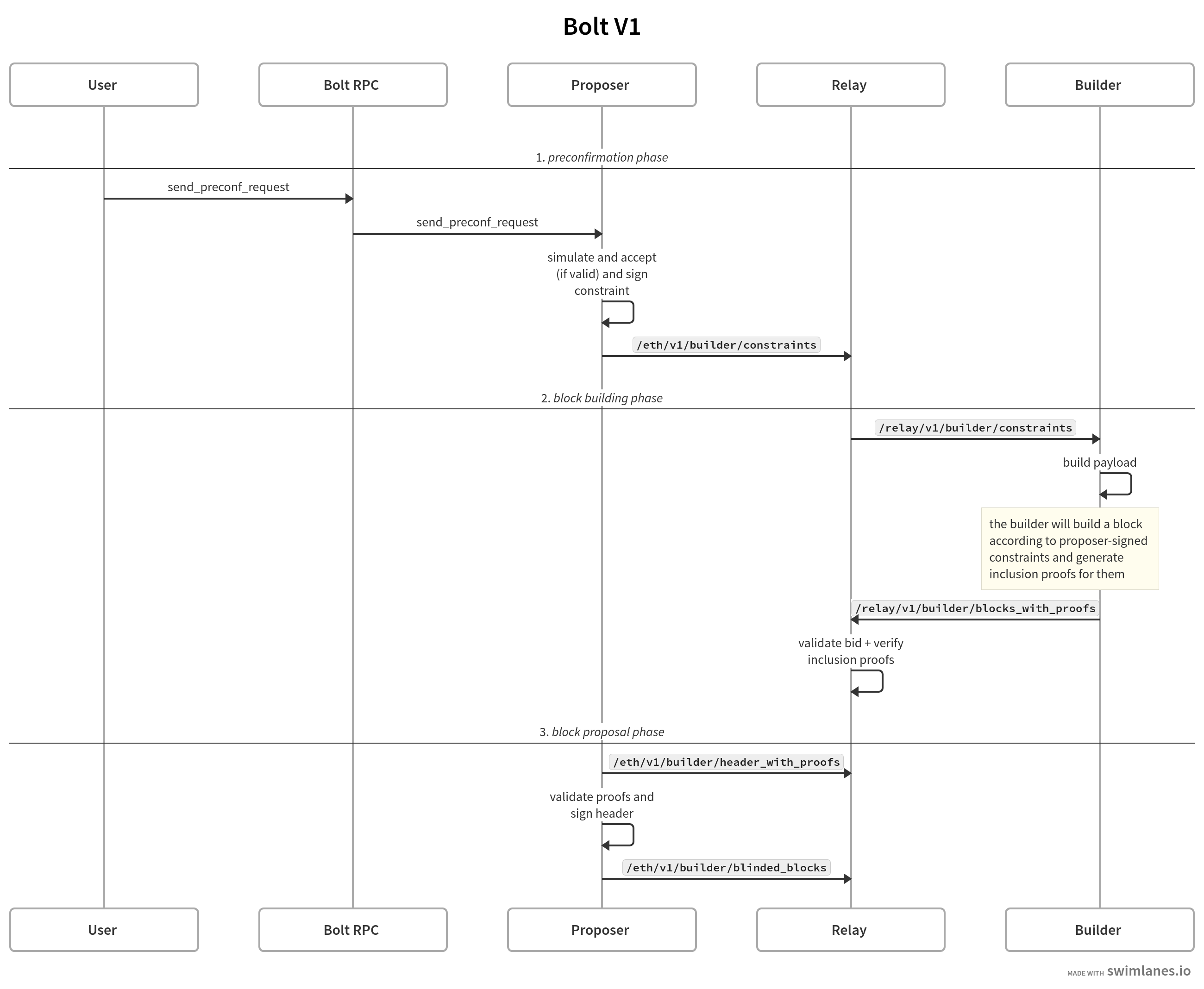
The specific steps are described as follows (from top to bottom):
- The User sends a preconfirmation request to the Bolt RPC 1.
- The Bolt RPC server (which implements the Commitments API) forwards the request to the Bolt opted-in Proposer next in line (according to the beacon lookahead window).
- The Proposer simulates the transaction and validates that it satisfies the protocol validity rules, such as the base-fee and nonce requirements. If the transaction is valid, the Proposer sends a signed preconfirmation back to the Bolt RPC to be relayed back to the User.
- The Proposer also shares the signed preconfirmation with the Relay, by calling its
/constraintsendpoint. - All Block builders subscribed to the Relay constraints SSE stream will receive the preconfirmation as an event.
- All Block builders build a payload which includes the preconfirmations and other transactions, as well as the constraint validity proofs. Then they submit the payloads to the Relay, along with these proofs.
- The Relay validates each bid along with its inclusion proofs (this step could also be skipped if running in optimistic mode).
- When it's time to propose, the Proposer calls the Relay's
/header_with_proofsendpoint to fetch the most profitable valid header. - Finally, the proposer also checks the validity of the header and its proofs, and if everything is correct, it signs it
and sends it to the Relay via the
/blinded_blocksendpoint. - At this point the relay has all the necessary information to submit the signed payload to the beacon chain.
Footnotes
-
The Bolt RPC does not need to be a single server, as it falls under the same conditions as regular Ethereum RPCs: anyone can run one. It's just a proxy server that implements the Commitments API. ↩